- Free delivery
- Oak caterpillar
- Presentation
- Formulation Gel - Cryptobiose
- Legal Notice
- Deliveries
- The main useful nematodes
-
Target pests
- Thrips
- Palm Butterfly (Paysandisia archon)
- The red weevil (Palm tree)
- Soil flies
- The ants
- Box tree moth
- Cutworm - cutworm caterpillars
- crane fly larvae
- The cutters
- White grubs, cockchafers
- Otiorhynchus
- Colorado potato beetle
- The plane tree tiger
- fruit codling moth
- mosquito larvae
- root aphid
- Slugs and snails
- The pear tiger - Stephanitis piri
- Tomato leaf miner
- Agave weevil
- Peach tree capnode
- Zeuzère of the fruit trees
- A little history ...
- Terms of Sales
- Contact us
- Professionnal work place
- Other pests
-
![ACA - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Acariens Acarien.info, products against mites
Acariens Acarien.info, products against mites -
![ANT - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Anthrène des tapis Acarien.info, products against mites
Anthrène des tapis Acarien.info, products against mites -
![ARA - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Araignee Acarien.info, products against mites
Araignee Acarien.info, products against mites -
![ARE - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Arrosage écologique Acarien.info, products against mites
Arrosage écologique Acarien.info, products against mites -
![CAF - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Cafards et Blattes Acarien.info, products against mites
Cafards et Blattes Acarien.info, products against mites -
![CAR - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Carpocapse (vers des fruits) Acarien.info, products against mites
Carpocapse (vers des fruits) Acarien.info, products against mites -
![CRO - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Charancon rouge du palmier Acarien.info, products against mites
Charancon rouge du palmier Acarien.info, products against mites -
![CHI - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Chats-Chiens Acarien.info, products against mites
Chats-Chiens Acarien.info, products against mites -
![LCV - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Chauve souris Acarien.info, products against mites
Chauve souris Acarien.info, products against mites -
![CHE - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Chenille Processionnaire Acarien.info, products against mites
Chenille Processionnaire Acarien.info, products against mites -
![DES - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Desherbage Acarien.info, products against mites
Desherbage Acarien.info, products against mites -
![DVB - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Désinfection-Virus-Bacterie Acarien.info, products against mites
Désinfection-Virus-Bacterie Acarien.info, products against mites -
![DIU - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Destructeur Insectes UV Acarien.info, products against mites
Destructeur Insectes UV Acarien.info, products against mites -
![EPI - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Equipement Protection Individuelle Acarien.info, products against mites
Equipement Protection Individuelle Acarien.info, products against mites -
![FNE - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Fouines Acarien.info, products against mites
Fouines Acarien.info, products against mites -
![FOU - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Fourmis Acarien.info, products against mites
Fourmis Acarien.info, products against mites -
![GUE - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Guêpes - Frelons Asiatique Acarien.info, products against mites
Guêpes - Frelons Asiatique Acarien.info, products against mites -
![ENG - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Les Engrais Acarien.info, products against mites
Les Engrais Acarien.info, products against mites -
![LIM - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Limaces Acarien.info, products against mites
Limaces Acarien.info, products against mites -
![TAU - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Lyon Taupe Acarien.info, products against mites
Lyon Taupe Acarien.info, products against mites -
![INS - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Maisons Insectes Acarien.info, products against mites
Maisons Insectes Acarien.info, products against mites -
![MAT - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Materiel de traitement Acarien.info, products against mites
Materiel de traitement Acarien.info, products against mites -
![MEP - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Mérule Acarien.info, products against mites
Mérule Acarien.info, products against mites -
![MIN - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Mineuse du Marronnier Acarien.info, products against mites
Mineuse du Marronnier Acarien.info, products against mites -
![MIT - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Mites des Vêtements - Alimentaire Acarien.info, products against mites
Mites des Vêtements - Alimentaire Acarien.info, products against mites -
![MOC - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Mouche cerise Acarien.info, products against mites
Mouche cerise Acarien.info, products against mites -
![OLI - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Mouche de l olive Acarien.info, products against mites
Mouche de l olive Acarien.info, products against mites -
![SUZ - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Mouche suzukii Acarien.info, products against mites
Mouche suzukii Acarien.info, products against mites -
![MDT - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Mouche-du-terreau Acarien.info, products against mites
Mouche-du-terreau Acarien.info, products against mites -
![MOU - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Mouches Acarien.info, products against mites
Mouches Acarien.info, products against mites -
![MTQ - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Moustique Acarien.info, products against mites
Moustique Acarien.info, products against mites -
![NEM - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Nématodes Acarien.info, products against mites
Nématodes Acarien.info, products against mites -
![NIC - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Nichoirs et Abris Acarien.info, products against mites
Nichoirs et Abris Acarien.info, products against mites -
![PAL - Acarien.info, products against mites]() palmiers Acarien.info, products against mites
palmiers Acarien.info, products against mites -
![PAY - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Papillon du palmier Acarien.info, products against mites
Papillon du palmier Acarien.info, products against mites -
![PHE - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Phéromone bio Acarien.info, products against mites
Phéromone bio Acarien.info, products against mites -
![PGE - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Pigeon Acarien.info, products against mites
Pigeon Acarien.info, products against mites -
![POU - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Poux rouges du Poulailler Acarien.info, products against mites
Poux rouges du Poulailler Acarien.info, products against mites -
![PDC - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Protection du cheval Acarien.info, products against mites
Protection du cheval Acarien.info, products against mites -
![PCR - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Pucerons Acarien.info, products against mites
Pucerons Acarien.info, products against mites -
![PUC - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Puces Acarien.info, products against mites
Puces Acarien.info, products against mites -
![PUL - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Pulvérisateur Acarien.info, products against mites
Pulvérisateur Acarien.info, products against mites -
![PUN - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Punaise de Lit Acarien.info, products against mites
Punaise de Lit Acarien.info, products against mites -
![PUR - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Purin Acarien.info, products against mites
Purin Acarien.info, products against mites -
![PYR - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Pyrale du buis Acarien.info, products against mites
Pyrale du buis Acarien.info, products against mites -
![SER - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Serpents Acarien.info, products against mites
Serpents Acarien.info, products against mites -
![SDA - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Soin des arbres Acarien.info, products against mites
Soin des arbres Acarien.info, products against mites -
![SDV - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Soin des végétaux Acarien.info, products against mites
Soin des végétaux Acarien.info, products against mites -
![SOU - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Souris - Rat - Campagnol - Rongeur Acarien.info, products against mites
Souris - Rat - Campagnol - Rongeur Acarien.info, products against mites -
![STO - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Stop Odeur Acarien.info, products against mites
Stop Odeur Acarien.info, products against mites -
![TIG - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Tigre du Platane Acarien.info, products against mites
Tigre du Platane Acarien.info, products against mites -
![CPT - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Tout Pour Le Compost Acarien.info, products against mites
Tout Pour Le Compost Acarien.info, products against mites -
![TPG - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Tout Pour Mon Gazon Acarien.info, products against mites
Tout Pour Mon Gazon Acarien.info, products against mites -
![PRU - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Ver de la prune Acarien.info, products against mites
Ver de la prune Acarien.info, products against mites -
![VRI - Acarien.info, products against mites]() Vrillette Acarien.info, products against mites
Vrillette Acarien.info, products against mites
-
Treating peach borer: Capnodis tenebrionis
How to identify the peach tree capnode?
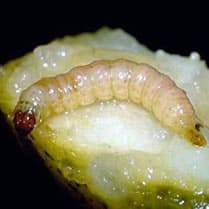
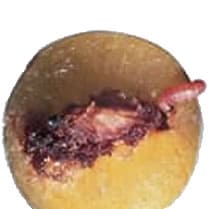
The peach tree borer ( Capnodis tenebrionis ) is a pest beetle that mainly attacks fruit trees, especially peach, apricot and almond trees. Native to Mediterranean regions, it is a major pest in orchards.
The capnode is easily recognizable thanks to:
- Size : Adults are about 2 to 3 cm long.
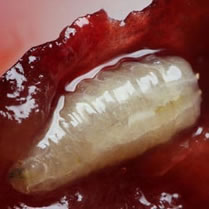
- Appearance : Adults have a black body with metallic sheen and a broad head. Larvae are white, legless and elongated, reaching 5 cm in length.
- Life cycle : Females lay their eggs at the base of trees or in crevices in the bark. The larvae penetrate the roots and dig galleries, causing significant underground damage.
Capnode larvae cause internal damage to tree roots, weakening trees and stunting their growth, while adults feed on young shoots and bark.
Presence of capnode in France
The peach tree capnode is mainly present in the Mediterranean regions of France, such as Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur , Occitanie and Corsica . It is particularly active during the warm months, from May to September.
Plants affected by peach borer
Peach trees and other fruit trees
Capnode mainly attacks stone fruit trees, such as:
- Peach trees ( Prunus persica )
- Apricot trees ( Prunus armeniaca )
- Almond trees ( Prunus dulcis )
- Cherry trees ( Prunus avium )
- Plum trees ( Prunus domestica )
Damage caused by the peach tree borer
Capnode larvae and adults cause significant damage to trees:
Galleries in the roots
The larvae dig deep galleries into the roots, which weakens the tree by disrupting the absorption of water and nutrients. This can cause general weakening and dieback of the tree.
Dieback of young shoots
Adults feed on young shoots and bark, causing branches to die back . Leaves turn yellow, and the tree may show signs of wilting.
Death of the tree
If the infestation is severe and untreated, capnodia can cause the death of trees within a few years, especially in young plants whose roots are more vulnerable.
Treatment with Steinernema Carpocapsae nematodes against peach borer
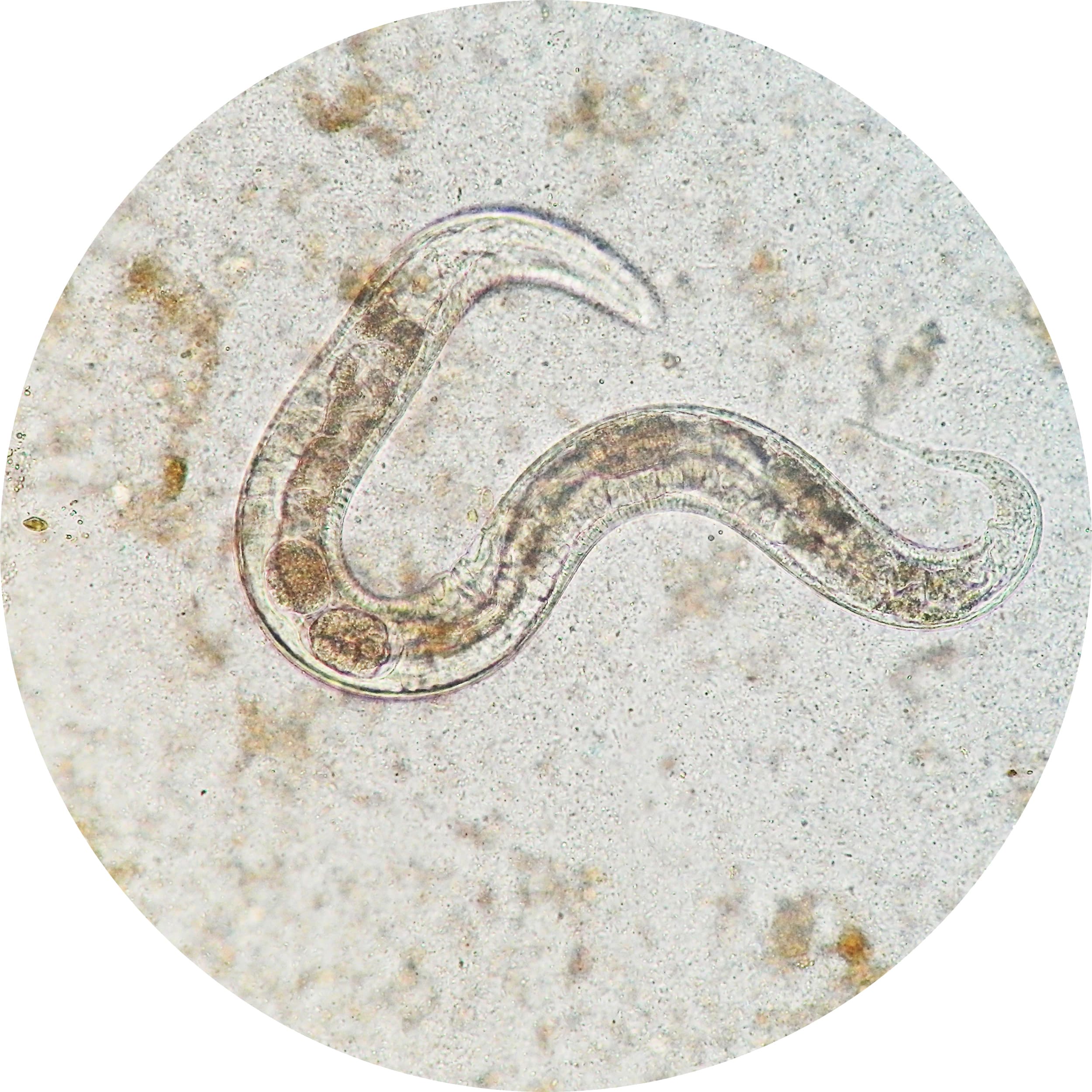 Nematodes are naturally present in the soil in small quantities, they are microscopic worms invisible to the naked eye, respectful of useful insects, crops and vertebrates (human beings and domestic animals). They are safe for dogs and cats.
Nematodes are naturally present in the soil in small quantities, they are microscopic worms invisible to the naked eye, respectful of useful insects, crops and vertebrates (human beings and domestic animals). They are safe for dogs and cats.
Steinernema Carpocapsae nematodes are microscopic worms used as a biological treatment against larvae. Their mode of action is simple but effective: once applied to the soil, the nematodes penetrate the larvae through natural channels and release symbiotic bacteria that destroy the inside of the larva, causing its death within a few days.
Nematodes do not have "legs", they move using water.
Delivery and storage of nematodes
Nemtodes can be delivered by non-refrigerated tracked letter directly to letter boxes up to 25 million.
Nematodes can survive more than 8 days at room temperature without any problem. Storing them in the fridge is just to be able to keep them longer by slowing down their development.
Nematodes should be kept cool after receipt in order to slow down their metabolism ("hibernation") so that they can be stored until the DLU date.
At room temperature, nematodes do not die but continue their development. Without food (larvae), they would eventually die naturally after about ten days.
Nematodes are supplied in the form of a more or less moist granular powder. The entire pot (or sachet) must be used in a single treatment to ensure uniform distribution and optimum effectiveness.
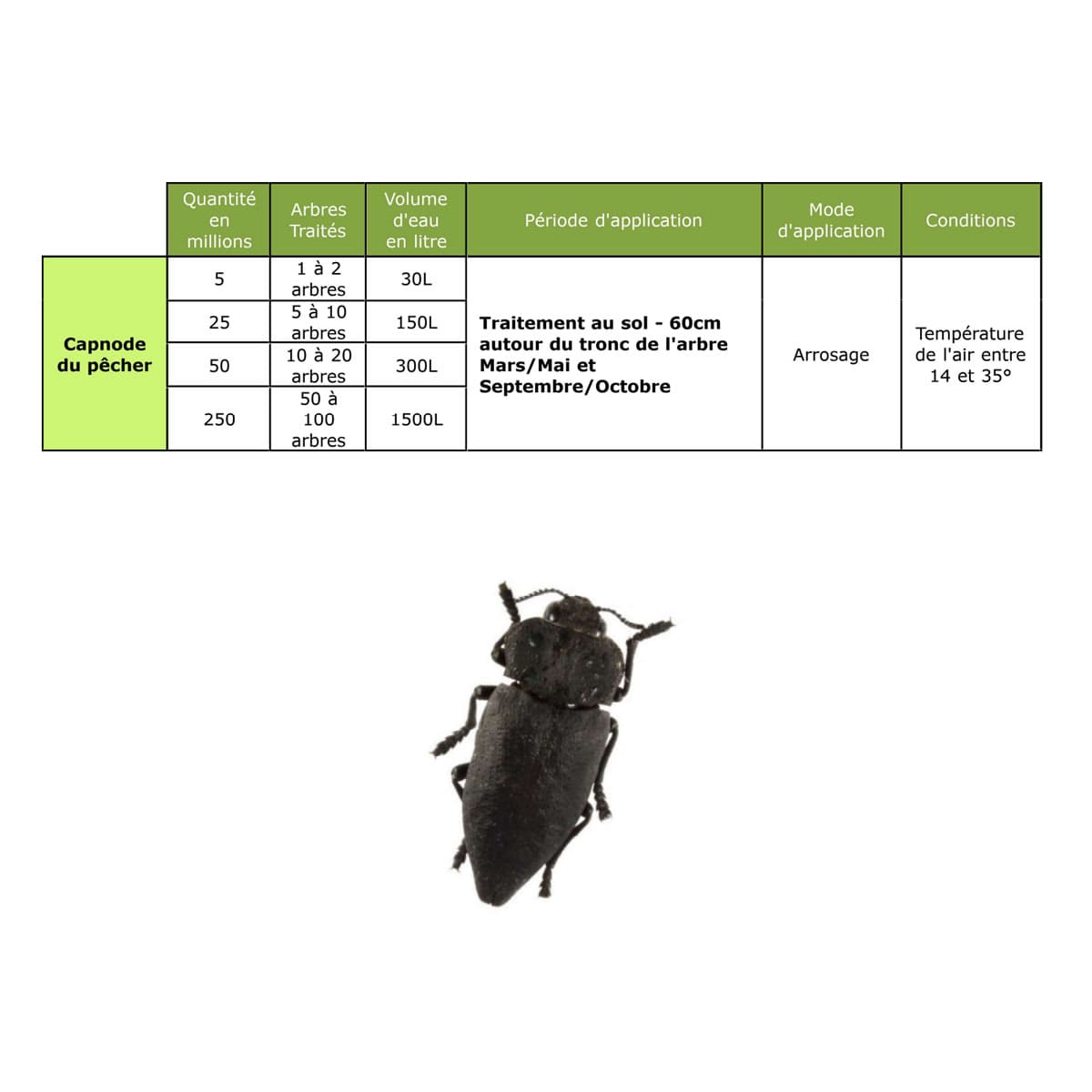
Available packaging of nematodes against the peach tree capnode SOLU'NÉMA
Steinernema Carpocapsae nematodes against peach borer are available in different packaging adapted to the surface to be treated:
Pot of 5 million nematodes for 1 to 2 trees
Pot of 25 million nematodes for 5 to 10 trees
Pot of 50 million nematodes for 10 to 20 trees
Bag of 250 million nematodes for 50 to 100 trees
PS: Pot containing a moist granular powder.
Dosage and application of nematodes
For maximum effectiveness, it is essential to dose the nematodes correctly according to the surface to be treated. Accurate dosage and good application allow all infested areas to be covered. Prepare a solution by diluting the nematode powder in clean water, then apply it to the potting soil, ensuring that the soil is moist to encourage their movement.
Instructions for use of nematodes against peach borer
1. Identify the Problem
The peach tree capnode is a robust beetle, measuring between 1.5 and 3 cm in length. It has an elongated body that is black or dark brown in colour, with elytra (hardened forewings) that can sometimes reflect metallic hues in certain lights. Adults are active during the summer months and are often attracted to light.
The life cycle of the peach tree capnode begins when the female lays her eggs in the soil, near the roots of the host trees. The larvae, once hatched, immediately begin to feed on the roots, tunneling inside and causing damage that can be severe. This larval phase can last up to two or three years, during which the larvae continue to feed and grow underground. Eventually, the larvae pupate in the soil before emerging as adults ready to reproduce and begin the cycle again.
Damage caused by the peach tree borer is mainly caused by the larvae, which attack the roots of fruit trees. This underground feeding can severely weaken or even kill young trees, reducing their ability to absorb water and nutrients. Heavily infested trees may show signs of decline, such as yellowing or wilting foliage, stunted growth and, in severe cases, death of the tree. Attacks on more mature trees can also reduce fruit production and the general vigor of the tree.
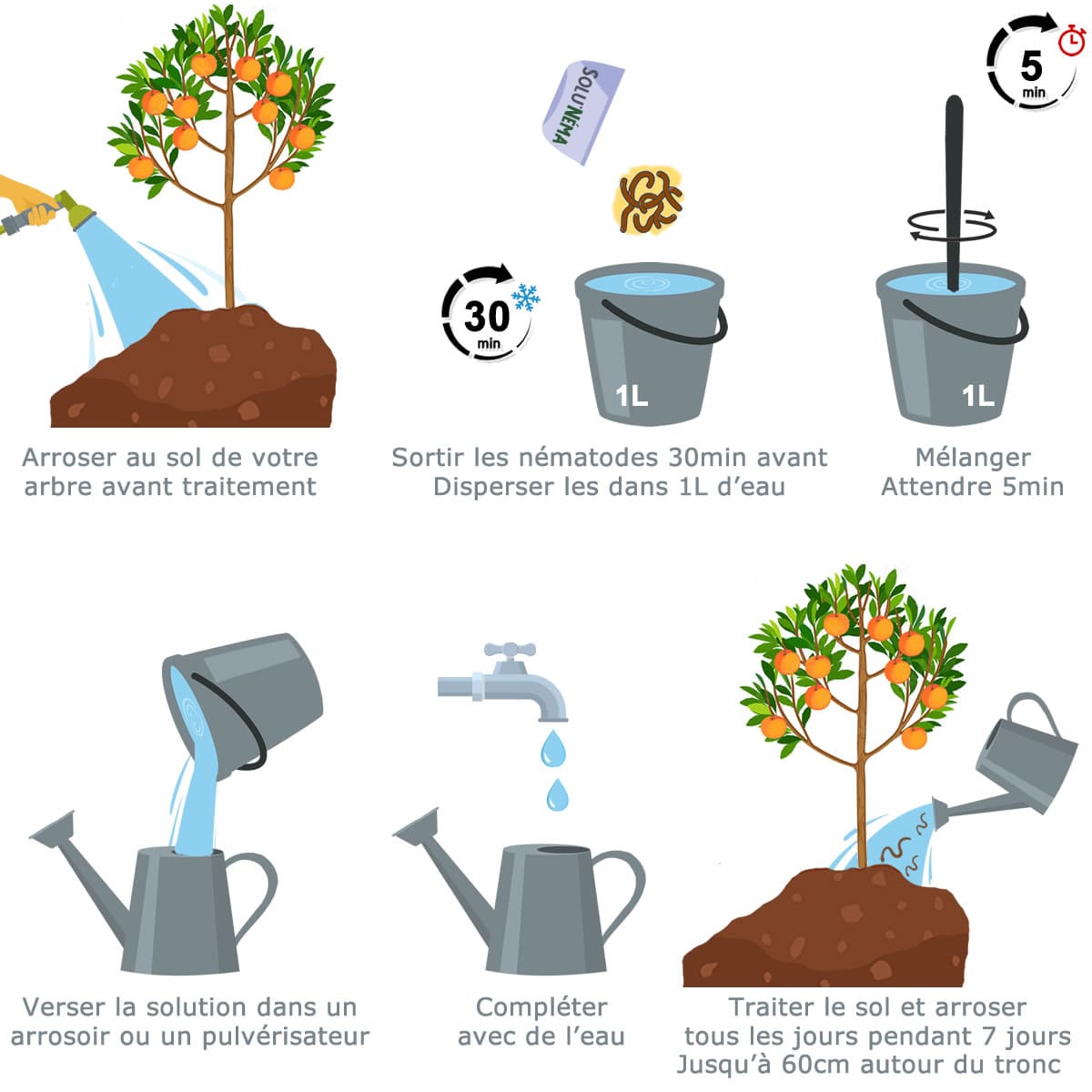
2. Preparation of Nematode Solution
Before use, leave the nematodes at room temperature for 30 minutes. Dilute the entire sachet in a small container of clean water at room temperature, pre-diluting the nematodes before mixing them. Stir well and let the contents dilute for 5 minutes. Then pour this preparation into your sprayer and add the rest of the water (between 15°C and 25°C). Mix again.
3. Spray Application of Nematodes
Moisten the soil before treatment to allow the nematodes to move more easily. Spray the nematode solution at the base of the tree and 60cm around it. Spray while continuing to agitate the mixture to prevent the nematodes from ending up at the bottom of the sprayer.
4. Continue Humidification
Nematodes require a moist environment to move to their prey. Water your crop regularly to maintain their effectiveness.
5. Monitor Results
Nematodes work quickly to control larvae. You should see a decrease in the larvae population after a few days. If larvae persist, repeat the treatment.
It is important to follow the application instructions to achieve the best results.
Prevention and advice against the peach tree borer
- Regular monitoring : Inspect trees regularly, especially the roots and the base of the trunk, to detect the first signs of galleries and the presence of sawdust.
- Crop Rotation : Avoid planting stone fruit trees in areas where capnode infestations have been reported.
- Soil maintenance : Aerate the soil around the trees and avoid excess humidity which encourages the development of larvae.